5 May 2025
What is Australia's Approach to AI Regulation?
As Artificial Intelligence (AI) continues to shape industries and societies worldwide, Australia has taken a cautious and evolving approach to regulation. AI is already contributing significantly to the nation's economy, with estimates suggesting it could add up to $315 billion to Australia's GDP by 2028. Unlike some regions, such as the European Union (EU), that have specific legislation tailored to AI, Australia’s AI laws are a work in progress.
For now, the country relies on voluntary frameworks and principles designed to encourage responsible AI use while supporting innovation. This blog explores Australia’s approach to AI regulation, recent developments, challenges, opportunities, and its position in the global AI regulatory landscape.
AI Regulation in Australia
Australia’s approach to AI regulation can be described as incremental and adaptive. While there is no overarching AI-specific legislation, several key elements characterise the current landscape and directly influence sectors such as mental health:
1. Voluntary AI Ethics Principles: Introduced in 2019, these principles encourage fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI use. For mental health professionals, these principles highlight the importance of ensuring that AI-powered diagnostic tools and platforms operate ethically.
2. Focus on High-Risk AI Use Cases: The Australian government prioritises oversight of AI applications that pose risks to safety, privacy, and public trust. Due to their sensitive nature, mental health applications of AI, such as therapy chatbots or predictive analytics, may fall under this category.
3. Interim and Ongoing Responses: Advisory bodies and consultations assess AI’s impact, enabling mental health professionals to provide feedback on how regulatory changes could shape their practices.
This regulatory approach aims to balance innovation with ethical considerations, ensuring safe AI deployment in sectors like mental health.
Key Voluntary Frameworks and Proposals
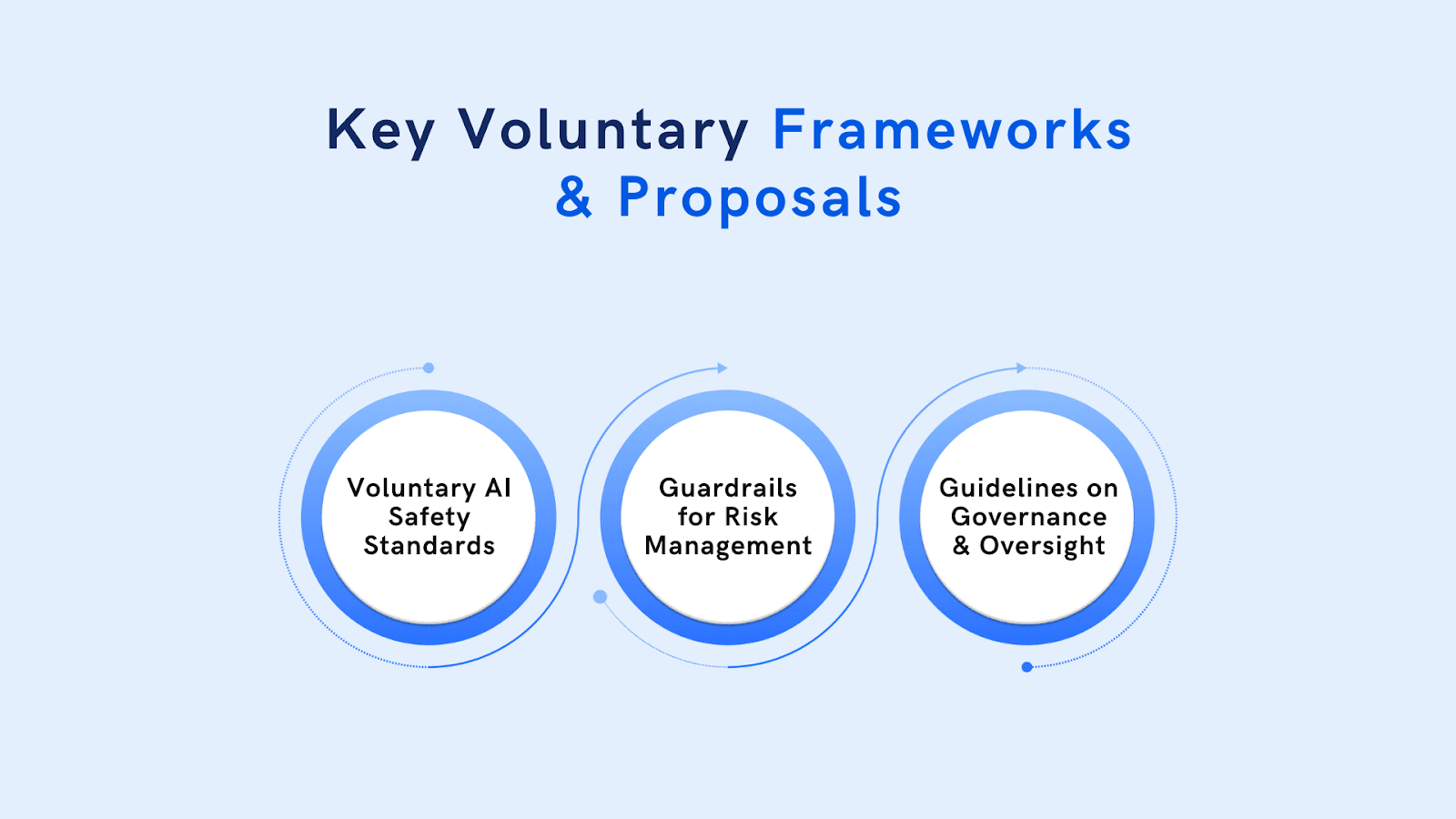
Australia’s voluntary measures establish foundational guidelines for AI deployment across industries, including mental health. These frameworks aim to align with ethical standards while supporting innovative practices.
1. Voluntary AI Safety Standards: These standards promote best practices for risk management, ensuring that tools like AI-driven mental health diagnostics meet quality and safety benchmarks.
2. Guardrails for Risk Management: Proposed guardrails focus on transparency, accountability, and ethical oversight, which are particularly relevant for mental health professionals using AI platforms to make sensitive decisions.
3. Guidelines on Governance and Oversight: Emphasising data governance, human oversight, and stakeholder engagement, support mental health practitioners in adopting AI responsibly while safeguarding patient trust and data security.
For mental health professionals, these frameworks provide a roadmap for integrating AI into practice without compromising ethical standards. Let us now explore the recent developments, challenges and opportunities in AI Regulation, which is important for you to understand to implement AI in your practice.
Recent Developments in AI Regulation
Australia’s recent initiatives reflect its commitment to refining AI governance, with implications for mental health care delivery:
1. Government Responses to AI Reports: Reports on AI risks and benefits have prompted targeted actions to ensure tools used in mental health adhere to ethical and safety standards.
2. Establishment of Advisory Bodies: Committees like the National AI Centre offer recommendations for industries, including healthcare, to guide safe AI integration into clinical workflows.
3. Influence of International Frameworks: By evaluating frameworks such as the EU AI Act, Australia ensures its regulatory approach remains globally aligned, benefiting mental health professionals adopting AI-driven tools.
These developments provide mental health practitioners with clearer expectations and resources for AI adoption.
Risks and Opportunities Associated with AI
AI offers immense potential benefits, but it also introduces significant risks. Understanding these opportunities and risks is essential for developing balanced regulatory approaches.
Risks
1. Bias in AI Systems: AI models trained on incomplete or biased datasets may perpetuate stereotypes, affecting diagnostic accuracy.
2. Data Privacy Concerns: Mental health data is highly sensitive, and breaches could erode patient trust.
3. Over-Reliance on Technology: Overuse of AI tools without sufficient human oversight could compromise the quality of care.

Opportunities
1. Enhanced Diagnostics: AI can analyse patient data to identify mental health conditions early, improving outcomes through timely interventions.
2. Personalised Treatment: Machine learning algorithms can tailor therapy plans to individual patient needs, enhancing effectiveness.
3. Increased Accessibility: AI-powered tools like chatbots make mental health support more accessible to underserved populations.
Mental health professionals must carefully weigh these opportunities and risks, advocating for ethical AI deployment and balancing these opportunities and dangers through targeted governance strategies and stakeholder collaboration.
How AI Regulation Could Affect Mental Health Professionals in Australia?
AI regulation in Australia is likely to have significant implications for mental health professionals, particularly as AI-driven tools and platforms become more prevalent in clinical practice. These impacts include opportunities for innovation and ethical considerations to ensure patient safety and data integrity.
1. Enhanced Diagnostic and Treatment Tools: AI-powered platforms can provide mental health professionals with sophisticated diagnostic tools and personalised treatment recommendations, improving patient outcomes. Regulation ensures that these tools meet safety and efficacy standards, protecting patients and clinicians alike.
2. Data Privacy and Security: Mental health professionals often handle sensitive patient data. AI regulations focusing on data governance and privacy will require compliance with stricter standards, ensuring that patient information remains secure and confidential.
3. Accountability and Transparency: AI systems used in mental health must be transparent and accountable. Regulations will likely mandate clear explanations of how AI algorithms work, helping professionals make informed decisions and maintain trust with their patients.
4. Training and Adaptation: As AI becomes integrated into mental health care, professionals will need to stay informed about regulatory requirements and best practices. This may involve training programs and certifications to ensure the ethical and practical use of AI technologies.
5. Ethical Considerations: The use of AI in mental health raises ethical questions, such as the potential for bias in algorithms and the role of human oversight. Regulatory frameworks will help address these concerns, ensuring that AI applications align with professional standards and patient-centric care.
For mental health professionals, adapting to AI regulation will involve balancing the benefits of innovative technologies with compliance and ethical responsibilities, ultimately enhancing the quality of care.
International Comparisons and Influences
Global trends and international frameworks shape Australia’s approach to AI regulation. Comparisons with other jurisdictions provide valuable insights:
1. EU AI Act: The EU’s comprehensive regulatory framework emphasises risk-based categorisation and strict compliance requirements for high-risk AI applications. Australia draws lessons from this approach while tailoring policies to its context.
2. US Strategies: The United States adopts a sector-specific and innovation-driven approach to AI governance, focusing on voluntary guidelines rather than comprehensive legislation.
3. Global Frameworks: Organisations such as the OECD and G7 influence Australia’s regulatory philosophy by promoting principles of transparency, accountability, and human-centric AI.
By engaging in global discussions, Australia ensures that its regulatory framework aligns with international best practices while addressing domestic priorities.
Future Directions for AI Regulation in Australia
The future of AI regulation in Australia involves a mix of public consultation, policy refinement, and potential legislative efforts. Key focus areas include:
1. Public Consultations: The government seeks input from stakeholders to refine guardrails and explore mandatory regulatory options for high-risk AI applications.
2. Development of Compliance Tools: Resources such as AI maturity models and risk assessment frameworks will help organisations meet emerging regulatory requirements.
3. Legislative Reforms: While voluntary measures dominate the current landscape, future efforts may involve updating existing laws or introducing new legislation to address AI’s unique challenges.
These efforts reflect Australia’s commitment to proactive and adaptive AI governance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Australia's current approach to AI regulation?
A: Australia relies on voluntary frameworks, such as the AI Ethics Principles, and focuses on regulating high-risk AI applications rather than implementing comprehensive legislation.
2. How do AI regulations impact mental health professionals?
A: AI regulations ensure the ethical and secure use of AI tools in mental health, emphasising data privacy, algorithm transparency, and patient safety.
3. What are the benefits of AI in mental health care?
A: AI offers enhanced diagnostic capabilities, personalised treatment plans, and increased accessibility to mental health services, particularly for underserved populations.
4. What risks should mental health professionals consider when using AI?
A: Potential risks include algorithmic bias, data privacy concerns, and over-reliance on AI tools, which could affect the quality of care and patient trust.
5. How can mental health professionals prepare for AI regulation?
A: Professionals can stay informed about emerging regulations, participate in training programs, and adopt best practices for ethical AI use in clinical settings.
6. How does Australia’s AI regulation compare to global approaches?
A: Australia’s regulatory approach is more voluntary and adaptive than that of the EU’s comprehensive AI Act. However, it aligns with global frameworks promoting transparency, accountability, and ethical AI practices.
Conclusion
Australia’s approach to AI regulation is a work in progress, reflecting the complexity and dynamism of the AI landscape. By relying on voluntary frameworks and emphasising high-risk governance, the country seeks to balance innovation with ethical responsibilities. However, as AI technologies evolve, Australia must remain agile, integrating insights from global regulatory developments and adapting its policies to meet emerging challenges.
Understanding and adapting to AI regulation is essential for mental health professionals to harness AI's potential while maintaining ethical and patient-centred care. PractaLuma’s AI Clinical Assistant allows mental health professionals to outsource repetitive note generation and report writing without breaching confidentiality. Check out PractaLuma here.