
1 April 2025
Understanding Case Formulation in Mental Health: Application and Use
“Formulation is the lynchpin that holds theory and practice together” (Butler, 1998).
Case formulation not only bridges the gap between diagnosis and treatment but also tailors therapeutic interventions to the unique complexities of each individual, leading to improved patient outcomes.
This blog breaks down the essential parts of case formulation, including its importance, how it’s done, and practical tips on using it in your clinical practice. First things first, let us look at what case formulation is.
What is Case Formulation?
Case formulation is a process that helps you gather, understand, and organise detailed patient information.
Unlike diagnosis, which labels as a set of symptoms, case formulation digs deeper to understand why those symptoms are present and how they affect the patient’s daily life. This approach provides a more rounded view of each patient, helping you create a treatment plan that targets the underlying causes, not just the symptoms.
1. Organising Patient Information in a Useful Way
Organising patient information clearly and practically is crucial in providing the best dental care. When records are well-structured and easy to access, it becomes much simpler to manage your workflow, communicate effectively, and offer personalised treatment to your patients. Here’s how you can organise patient information to make your practice run more smoothly.
2. Creating and Testing Hypotheses About the Patient’s Needs
In case formulation, developing “hypotheses” is about understanding the reasons behind a patient's issues. You might see patterns of thought, behaviour, or feelings contributing to their challenges. For example, a patient who avoids social situations might experience worsening anxiety. By identifying these patterns, you can choose therapies that help address the specific causes of a patient's difficulties.
Why is Case Formulation Essential?
Case formulation for mental health is essential because it provides a roadmap for personalised treatment. By uncovering the unique factors influencing a patient’s mental health, clinicians can create targeted, effective plans beyond diagnosis, ultimately improving patient engagement and outcomes.
1. Acts as a Guide for Treatment
Case formulation serves as a guide, allowing you to choose treatment options that directly address the root causes of the patient’s challenges. This focused approach helps organise therapy sessions, ensuring that every step in the treatment process is intentional and effective.
2. Fosters a Shared Understanding
Another significant benefit is that case formulation creates a shared understanding between you and the patient. By discussing the formulation, you can explain why specific therapies are recommended. This transparency helps patients understand their treatment journey, which can increase their engagement and trust in the process.
3.Tailoring Care Beyond Diagnosis
Where a diagnosis might provide a general understanding of a disorder, case formulation gives a detailed, personalised view. You gain insights into each patient’s unique experiences and strengths, allowing you to design specific treatments. This approach can improve outcomes since the treatment aligns closely with the individual’s needs. Now that we know how essential case formulation is for mental health patients let us explore the major components (The Five P’s) of case formulation.
Critical Components of Case Formulation: The “Five P’s”

The "Five P's" model is a powerful tool in mental health case formulation, breaking down essential aspects of patient experience. Each component offers a unique piece of the puzzle, helping clinicians understand what the patient is dealing with and why and how these issues are maintained. Here’s a quick guide to the Five P’s:
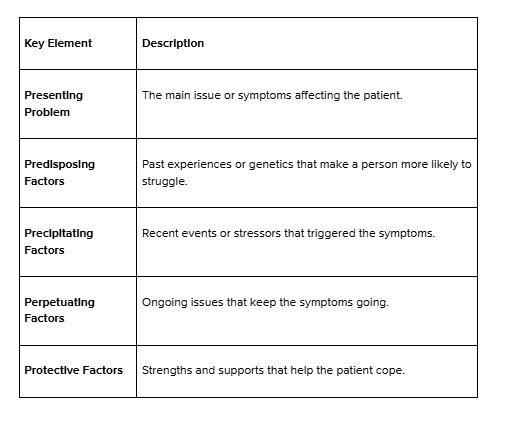
1. Presenting Problem: Identifying Key Issues
The presenting problem pinpoints the specific issues or symptoms affecting the patient. Going beyond a simple diagnosis, it focuses on the main difficulties impacting the patient’s life, such as anxiety, low mood, or relationship struggles. This clear identification helps direct the treatment approach toward what matters most to the patient.
2. Predisposing Factors: Exploring Vulnerabilities
Predisposing factors are historical or personal elements that make the patient more vulnerable to mental health challenges. These can include genetic influences, early life experiences, or personality traits. By understanding these long-term influences, clinicians gain insights into the factors that may have shaped the patient’s struggles.
3. Precipitating Factors: Recognising Triggers
Precipitating factors are recent events or changes that may have triggered the onset or worsening of symptoms. Common examples include job loss, relationship breakups, or significant life stressors. Identifying these triggers provides context for the patient’s recent experiences, allowing targeted early interventions.
4. Perpetuating Factors: Breaking the Cycle
Perpetuating factors are behaviours, thoughts, or circumstances that sustain the patient’s symptoms. These could include avoidance behaviours, ongoing stressors, or negative thought patterns. Recognising these elements allows clinicians to address and reduce the factors keeping symptoms alive.
5. Protective Factors: Building on Strengths
Protective factors are the patient’s strengths and resources supporting their coping ability. These might include a robust social network, positive coping skills, or personal resilience. By leveraging these strengths in the treatment plan, clinicians can help patients build on what’s already working well, fostering long-term resilience.
Developing and Using Case Formulation
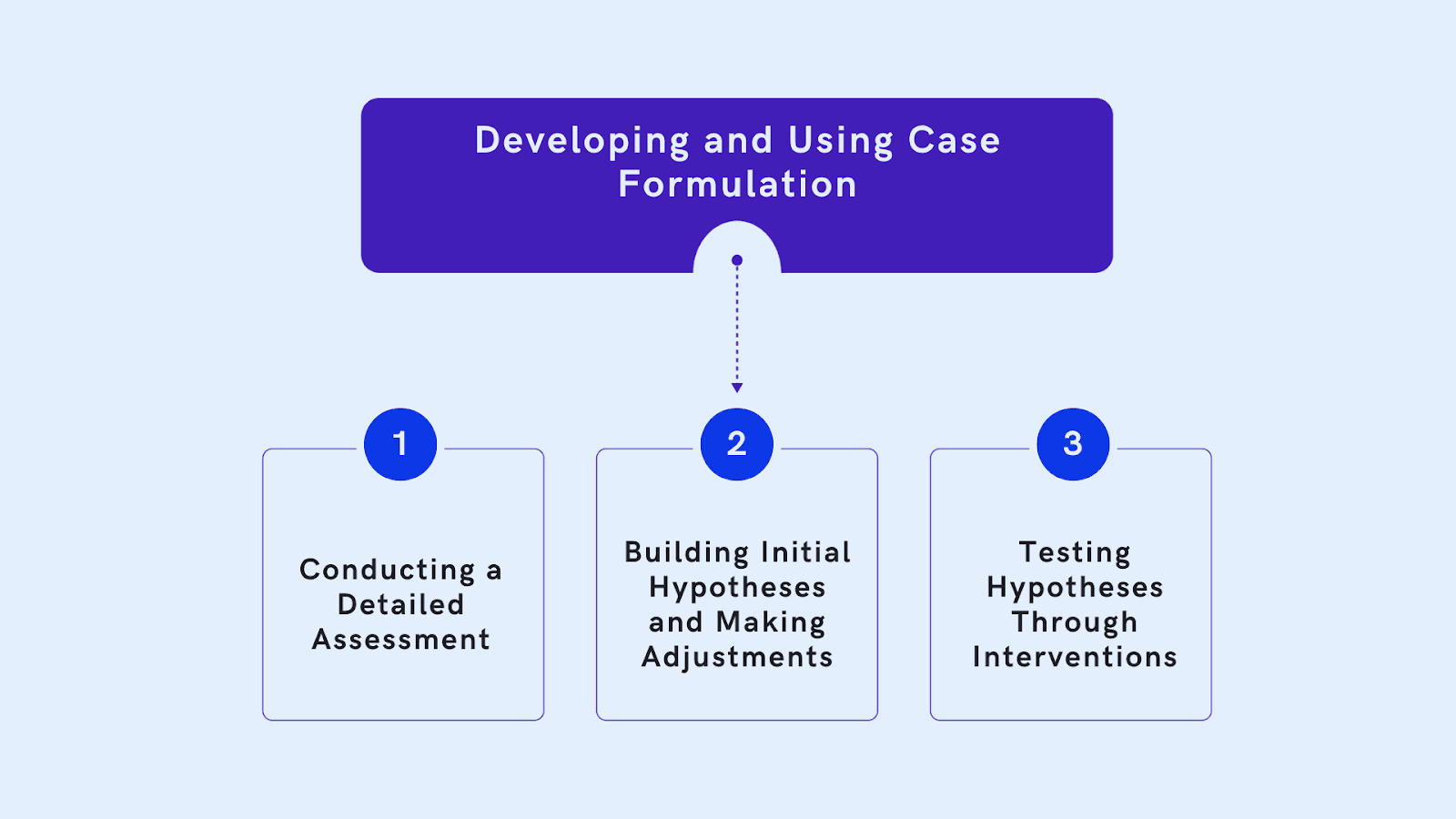
By systematically identifying key factors affecting a patient, clinicians can design targeted interventions that address root causes and support lasting progress. Some tips that will help develop case formulation include:
1. Conducting a Detailed Assessment
A solid case formulation starts with a thorough assessment. This involves clinical interviews, questionnaires, and input from people close to the patient. A full assessment helps ensure you cover all aspects of the patient’s life, from personal history to current issues, giving you a complete picture.
2. Building Initial Hypotheses and Making Adjustments
Once you’ve gathered information, you can create initial hypotheses. This means forming ideas about what might be causing and maintaining the patient’s symptoms. These are used as a starting point for treatment, and they can change as new information becomes available. Case formulation should be flexible so it stays relevant as the patient progresses.
3. Testing Hypotheses Through Interventions
You can test your initial hypotheses by implementing specific interventions. For example, if a patient’s anxiety seems linked to avoidance behaviours, gradual exposure to feared situations might be helpful. Observing how the patient responds will help you refine the formulation over time, ensuring it stays aligned with their needs.
Utilising AI can significantly assist in the development of case formulation. Practaluma is an excellent solution for you to consider.
Techniques in Case Formulation
Case formulation is an ongoing process in therapy, integrating continuous assessment, informal and standardised techniques, and structured models like the Five P’s to develop a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s needs and progress.
1. Continuous Assessment
Assessment isn’t a one-time event; it’s a continuous part of effective therapy. By regularly checking in with the patient and reassessing their progress, you can adjust the formulation to keep it relevant. This approach ensures that treatment remains aligned with the patient’s ongoing experiences.
2. Blending Informal and Standardised Techniques
Combining informal interviews with structured assessments gives you a rounded view of the patient. Informal techniques provide personal insights, while standardised assessments offer objective data that confirm and enrich the formulation.
3. Using the “Five P’s” Model
The “Five P’s” model—Presenting, Predisposing, Precipitating, Perpetuating, and Protective factors—is a structured approach that helps you categorise and systematically organise patient information. This model ensures that no critical aspect of the patient’s story is overlooked, helping you form a complete picture of their situation.
Building Skills in Case Formulation
Mastering case formulation requires specialised skills that can be strengthened through training and professional development.
Expanding your knowledge of psychological patterns and learning how to bring different information sources together can improve your effectiveness as a clinician. Practising these skills supports a deeper understanding of complex cases, allowing for better patient care.
Critical Skills for Effective Case Formulation :
- Active Listening: Fully understand patient concerns.
- Analytical Thinking: Identify patterns and root causes.
- Collaboration: Work with patients and other professionals.
- Adaptability: Update formulations as new information arises.
- Problem-Solving: Develop targeted, effective treatment plans.
- Empathy: Build trust with a compassionate approach.
- Clear Communication: Document and explain formulations clearly.
Let’s look at a real-life example to understand case formulation and how it works in actual practice.
Real Life Case Study
The “Five P’s” model provides a structured approach to understanding a patient’s mental health profile. Here’s how it might apply to Rachel, a young 30-year-old woman experiencing social anxiety. This model helps map out Rachel's unique experiences, focusing on factors contributing to her symptoms, maintaining them, and supporting her resilience.
Rachel’s Case Formulation Using the “Five P’s” Model
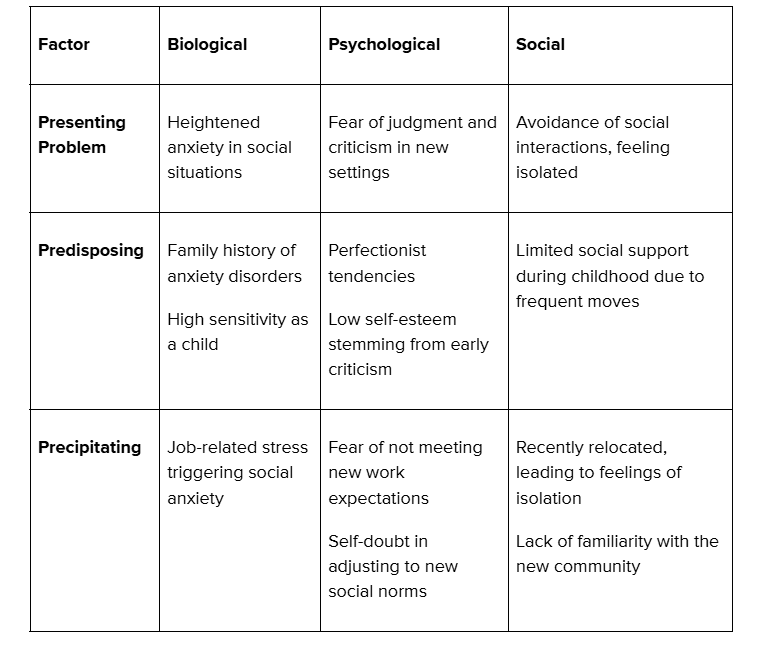
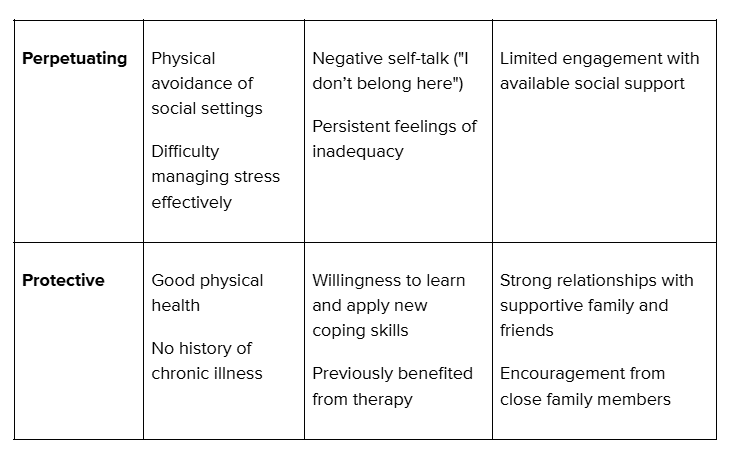
Explanation of Rachel’s Case Components
- Presenting Problem: Rachel's main issue is social anxiety, particularly in situations where she fears judgment from others. This leads her to avoid social interactions, further increasing her sense of isolation.
- Predisposing Factors: Rachel has a family history of anxiety and a naturally sensitive personality. Early experiences with criticism and perfectionist tendencies may make her more prone to social anxiety.
- Precipitating Factors: Recent job-related stress and relocation to a new community triggered Rachel’s anxiety. These changes caused her to feel self-conscious and unsure about fitting in, especially with new colleagues and community members.
- Perpetuating Factors: Rachel’s habit of avoiding social situations reinforces her anxiety and negative self-perception. Negative thoughts and feelings of inadequacy create a cycle that sustains her symptoms, keeping her in isolation.
- Protective Factors: Rachel has strong family support, good physical health, and past success with therapy. Her openness to trying new coping strategies and encouragement from family members provide a solid foundation for her recovery.
Using the “Five P’s” model, clinicians can develop a well-rounded treatment plan tailored to Rachel’s needs. This approach supports the creation of targeted interventions, addressing her vulnerabilities and strengths to guide her toward meaningful progress.
Conclusion: Enhancing Patient Outcomes with Case Formulation
For allied health professionals, case formulation is a practical, effective tool for understanding and addressing complex mental health issues. You can create personalised treatment plans beyond diagnosis by considering many factors, including strengths and challenges. Case formulation allows for ongoing assessment and adaptation, helping you offer better, more responsive care to every patient.
With tools like Practaluma’s Automated Report Writing, you can streamline the documentation process, saving time while keeping all critical patient information secure and organised.
Start using Practaluma to make case formulation easier and more effective for your practice.