13 March 2025
Data Privacy Challenges and Solutions in the Age of AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionising industries, transforming data-driven decision-making, and unlocking unprecedented insights. However, these advancements also introduce complex privacy challenges that must be carefully navigated for mental health professionals.
The large-scale collection, processing, and use of personal information in AI systems raise unique concerns for safeguarding sensitive patient data. This article explores these challenges, risks, and strategies to ensure data privacy in the AI age, specifically tailored for mental health professionals.
Understanding these privacy concerns is crucial for mental health professionals, as the ethical use of AI hinges on balancing technological advancements with the responsibility to protect patient confidentiality. Let’s delve deeper into the specific challenges posed by AI in safeguarding sensitive data.
AI Privacy Challenges
AI systems rely heavily on data to function effectively. However, the ways in which this data is collected, used, and managed raise significant privacy concerns for mental health professionals handling sensitive patient information.
1. Privacy Concerns in Data Collection: AI often requires vast amounts of data collected from diverse sources. These methods can lead to the unintentional collection of personal or sensitive information, raising questions about patient consent and transparency.
2. Sensitive Information Use: Mental health records, often rich in personal details, are particularly vulnerable when processed by AI. Predictive models might inadvertently expose sensitive patient insights, creating risks for misuse or breach.
3. Ethical Implications: Using AI-based decision-making in mental healthcare, such as predictive analytics for treatment planning, introduces ethical dilemmas. These systems may inadvertently reinforce biases or make opaque decisions, complicating trust and accountability in patient care.
Understanding these challenges is the first step toward addressing the complex relationship between AI and data privacy.
Key Risks Posed by AI Systems
AI systems intensify traditional privacy risks while introducing new vulnerabilities unique to their capabilities and applications.
1. Traditional Privacy Risks: AI amplifies existing issues related to data control, such as unauthorised access, data breaches, and the difficulty of withdrawing consent for data use once it has been collected.
2. Anti-Social Data Uses: Generative AI poses specific risks, such as deepfakes or malicious content creation, that can compromise individual privacy and societal trust.
3. Unintended Consequences of Data Repurposing: AI's capacity to derive insights from seemingly unrelated datasets can lead to the unintentional repurposing of data, creating new risks for individuals whose data was initially collected for different purposes.
Recognising these risks allows mental health professionals to implement targeted safeguards, ensuring patient data remains protected.
Unique Privacy Challenges of AI
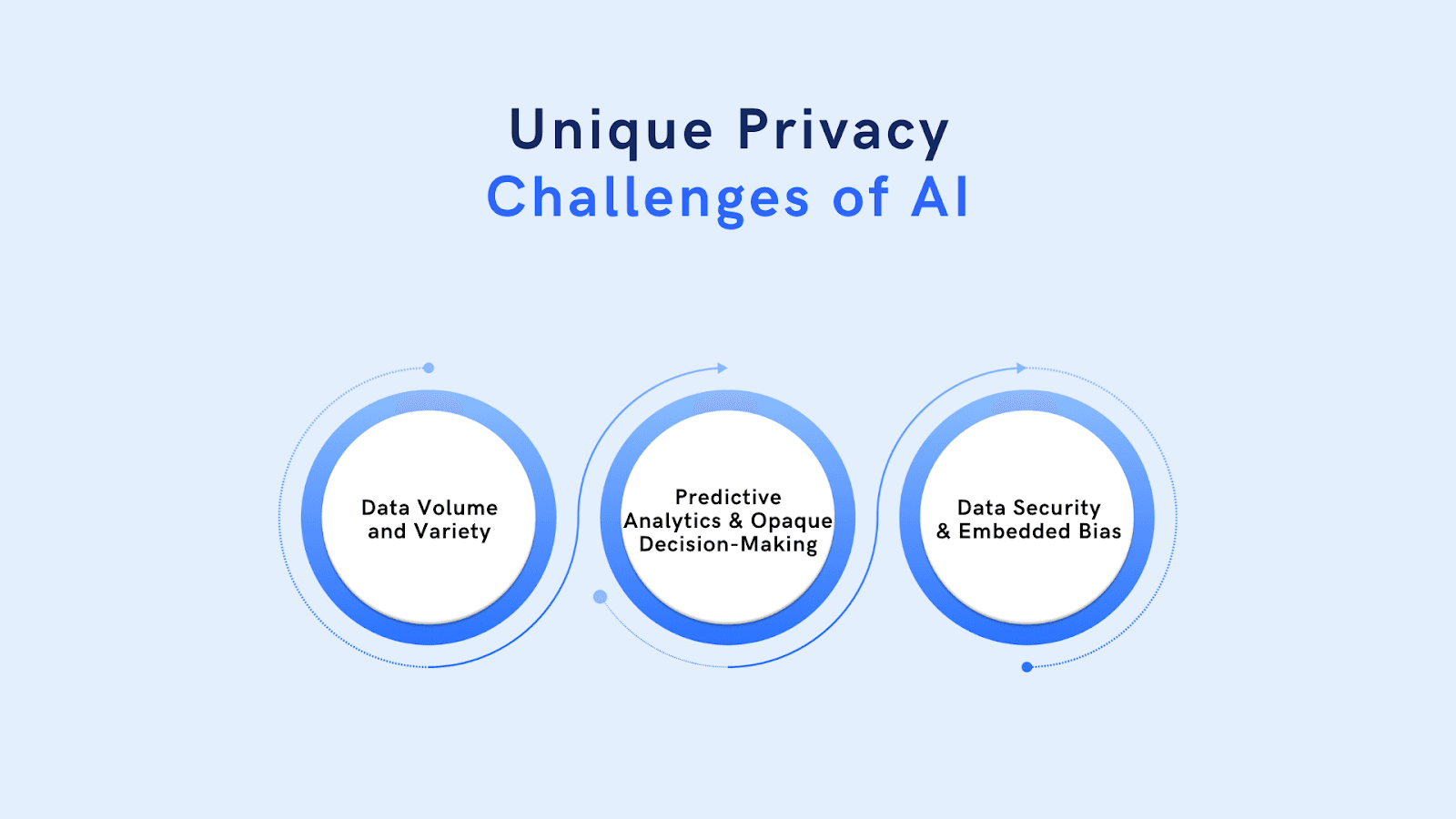
AI introduces distinct privacy challenges due to the scale and complexity of its operations.
1. Data Volume and Variety: AI systems require massive datasets, often drawn from diverse sources. This increases the likelihood of inadvertently processing personal or sensitive information, making it harder to ensure compliance with privacy laws.
2. Predictive Analytics and Opaque Decision-Making: AI-driven insights can be challenging to interpret or explain, creating transparency issues. For mental health professionals, for example, predictive analytics might raise concerns about how conclusions are reached.
3. Data Security and Embedded Bias: Large datasets are prone to security vulnerabilities, and bias in AI systems can disproportionately impact certain groups, further complicating privacy issues.
These challenges demand innovative solutions that go beyond traditional data privacy measures.
Regulatory Frameworks and Efforts
Regulations play a critical role in addressing privacy challenges, but gaps and inconsistencies across jurisdictions create obstacles for businesses and professionals alike.
1. Global Regulations Overview: Frameworks such as the Australian Privacy Act and the European Union's 2019s GDPR provide guidelines for data privacy, setting benchmarks for how personal information should be managed.
2. Regulatory Gaps: Despite these efforts, AI-specific privacy concerns, such as algorithmic transparency and accountability, often fall outside the scope of existing regulations. This creates challenges for organisations attempting to ensure compliance.
3. Shaping Data Practices: Regulatory efforts are increasingly focused on shaping responsible AI practices, encouraging organisations to adopt privacy-by-design principles, and giving individuals greater control over their data.
For AI-driven industries, navigating these regulatory landscapes is essential to building trust and ensuring ethical data use.
Strategies for Mitigating AI Privacy Risks
To address AI privacy risks, organisations must adopt proactive strategies that prioritise transparency, control, and security.
1. Embedding Privacy by Design: Integrating privacy considerations into the design of AI systems ensures that privacy safeguards are built into every stage of the development process.
2. Data Anonymisation and Aggregation: Transforming raw data into anonymised or aggregated formats reduces the risk of identifying individuals while maintaining the usefulness of data for AI analysis.
3. Increasing Transparency: Providing users with clear information about how their data is collected, processed, and used empowers them to make informed decisions and enhances trust in AI systems.
Implementing these strategies helps organisations align with evolving privacy expectations and regulatory requirements.
Proposed Solutions to Data Privacy Issues
Building on current strategies, innovative solutions can help organisations address emerging challenges in AI data privacy.
1. Opt-In Mechanisms: Shifting from opt-out to opt-in data collection mechanisms ensures that individuals provide explicit consent for their data to be used, enhancing trust and compliance.
2. Supply Chain Privacy Management: Organisations must ensure that all entities in their data supply chains adhere to robust privacy standards, safeguarding data across its lifecycle.
3. Ethical AI Cultures: Cultivating an organisational culture that prioritises ethical AI use encourages transparency, accountability, and fairness in all AI applications.
These solutions help maintain ethical and privacy-focused practices in mental healthcare.
Collective Data Privacy Solutions
While individual-focused solutions are essential, collective efforts offer additional opportunities to strengthen data privacy in AI.
Over-reliance on individual consent places a disproportionate burden on users, highlighting the need for systemic approaches to privacy protection. Trusted intermediaries can manage data on behalf of individuals, ensuring compliance with privacy laws while enabling the benefits of AI-driven insights.
By shifting the focus from individual responsibility to collective accountability, organisations can create more sustainable and equitable data privacy solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the main data privacy challenges in AI for mental health professionals?
AI systems in mental health often involve sensitive patient data, creating challenges such as ensuring consent, preventing data breaches, and addressing ethical concerns related to AI-driven decision-making.
2. How can mental health professionals ensure AI tools align with privacy regulations?
Professionals can ensure compliance by adopting privacy-by-design principles, anonymising patient data, and staying informed about evolving privacy regulations like GDPR and Australia’s Privacy Act.
3. What is the significance of transparency in AI-driven mental healthcare?
Transparency helps build trust by providing patients with clear information about how their data is collected and used, enabling them to make informed decisions.
4. How does data anonymisation support privacy in mental healthcare AI?
Anonymisation reduces the risk of re-identifying patients from datasets, allowing AI tools to generate insights without compromising individual privacy.
5. Why is ethical AI important in mental healthcare?
Ethical AI ensures that AI systems prioritise fairness, accountability, and transparency, minimising bias and safeguarding the trust of patients and professionals.
6. What role do data intermediaries play in mental health data privacy?
Data intermediaries securely manage sensitive information on behalf of mental health organisations, ensuring compliance with privacy laws and reducing risks of data misuse.
Conclusion
As AI continues to transform industries, reinterpreting privacy principles for the digital age is crucial. Ethical data stewardship, emphasising transparency, accountability, and fairness, must become a cornerstone of AI development and deployment.
By prioritising privacy-by-design principles and collective solutions, we can harness AI potential while protecting individuals' rights and dignity in an increasingly data-driven world. PractaLuma’s Secure Document Storage keeps your patients’ data private, helping you reap all that the age of AI has to offer without compromising security. Check out more about PractaLuma here.